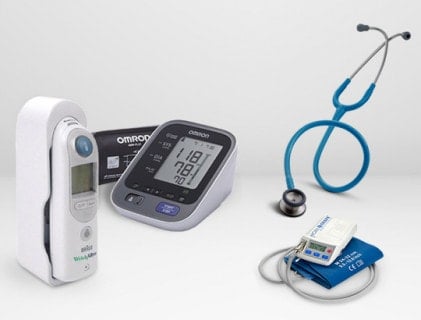
Healthcare pros use diagnostic medical tools and materials. They help measure and check a patient’s health. This helps doctors figure out what’s wrong. After figuring it out, they can give the right treatment. You can find these tools in outpatient care places. They are for both adults and kids. They are also in ERs, hospital rooms, and ICUs. The next list is not full, but it shows some of the most used diagnostic tools.
1. Auscultation Devices:
What do we first notice about doctors? Their stethoscope, right? It’s the most iconic medical tool. Doctors use it to listen to what’s happening inside us. It picks up sounds from our heart, lungs, and blood flow in our veins. Known as auscultation devices, they help doctors understand our health better. These devices are super important. They help doctors find things that might be wrong with our health by listening to our body’s internal sounds.
Key Features of Auscultation Devices:
Heart Sounds Monitoring:
Auscultation devices are primarily designed to capture and interpret heart sounds. By placing the device on different areas of the chest, healthcare professionals can listen to the rhythmic beats, identifying irregularities, murmurs, or other abnormalities.
Lung Sound Analysis:
These tools help check lung sounds. This is useful in spotting issues with breathing. Sounds like wheezing, strange noises, or weak breath sounds show up when using these tools carefully.
Studying Blood Flow:
These tools help doctors check blood flow in veins and arteries. When they put the tool over certain areas, they can find problems like abnormal noises or irregular blood flow.
Diagnostic Applications:
Listening to the heart and lungs is vital. It helps to spot problems like heart murmurs, valve troubles, lung infections, and lung diseases. This key step guides us in understanding a patient’s health. Tools used for this listening are crucial in health check-ups. They give important information about how the body’s inside parts are working. As these tools evolve, they get better at spotting diseases, leading to top-notch patient care.
Synonyms: Listening Devices, Heart Monitors
2. Blood Pressure Gauges:
Explanation:
Blood pressure gauges are important. They measure blood pressure and help find health problems. Blood pressure gauges have other names. Some people call them sphygmomanometers or blood pressure monitors. These are very important tools that doctors use to check on the pressure of blood in our bodies. They tell us about heart health and are used a lot by health professionals to check and monitor patients. Now, let’s talk about the important parts of Blood Pressure Gauges:
Blood Pressure Measurement:
Blood pressure monitors are tools built to check two key numbers: systolic pressure (the force with each heartbeat) and diastolic pressure (the force during the pause between heartbeats). Normally, it’s expressed like systolic over diastolic. For example, 120/80 mmHg. Checking for High and Low Blood Pressure: Using these monitors, we can spot both hypertension (high blood pressure) and hypotension (low blood pressure). Both are important signs of heart health. Regular checking aids in early discovery and handling of these health issues.
Checking Arteries:
By looking at blood pressure, we can learn about artery health. This can alert us to issues like stiff arteries or buildup of plaque. It can even flag other heart problems. Finding Health Problems: Keeping an eye on blood pressure can help find diseases. It can reveal issues like diabetes or certain kidney diseases. These might change your blood pressure. How Accurate Are They?: Manual blood pressure devices with mercury are seen as very accurate. Aneroid devices also work well but may need to be checked to make sure they’re accurate more often.
Digital versions offer ease of use and portability but may have slightly lower accuracy compared to manual counterparts.
You can also use a blood pressure gauge at home. It allows you to keep an eye on your blood pressure. People with high blood pressure or heart problem risk will find this useful.
It Can Work with Other Health Tools:
Newer blood pressure monitors can connect with other health tools or phone apps. This gives you a full look at your health and keeps track of your data. Blood pressure monitors are important for stopping health problems before they start. They help find issues with the heart early on and help to manage them. Make sure to check your blood pressure often. It’s key for heart health and for stopping issues linked to high and low blood pressure.
Synonyms: Sphygmomanometers, Blood Pressure Monitors
3. Ocular Inspection Tools:
Description:
Ophthalmoscopes, which are tools used for eye exams, are handheld. They help doctors closely inspect a patient’s eye. You may also hear them referred to as ocular inspection tools or fundus scopes. They play a key role in health care. Their job? To look closely at the inside of a patient’s eyes. These tools let us get a good look at the eye and help to track and diagnose eye problems.
Key Features of Ocular Inspection Tools:
Fundus Examination:
Eye checking tools help doctors look closely at the fundus. This includes the retina, optic nerve head, and blood vessels. It’s a very important check. These handheld tools help spot issues like diabetic or hypertensive retinopathy, and other eye problems. They let healthcare experts see close-up views of the back part of your eye, the fundus. That allows them to check the tiny details of the eye’s inside parts. It’s useful in spotting abnormal bits, changes, or hints of sickness.
Direct and Indirect Ophthalmoscopy:
There are two main kinds of eye check tools, direct and indirect ophthalmoscopes. Direct ophthalmoscopes create a larger, right way up image. They work best when close to the patient’s eye, ideal for detailed checks. On the other hand, indirect ophthalmoscopes make a smaller, upside-down image. These are good for patients with clouded eyes as they can be used from a bit far away.
Diagnosis of Eye Conditions:
Eye tools are crucial for spotting different eye problems. These might be bacterial diseases, loose retinas, or glaucoma. They can even find other disorders of the retina. Seeing these issues early is really important. This can help eye doctors to give quick help and care.
Light Source and Illumination:
Eye check-up tools have bright lights. They light up the inside of your eye. This light is important. It helps us see the back of your eye and spot anything unusual there.
Integration with Imaging Technologies:
Eye check-up tools can work with picture-taking tech to get very sharp pics or videos of the back of the eye. These can be saved for records, checking changes, or chats with experts.
Training and Education:
Eye exam tools are key in medical learning. They help students and health experts get better at testing eyes. These tools make learning about eye parts and diseases more hands-on.
In the eye care field, these tools are a must. They let doctors gather important data on a patient’s eye health. These devices aid in finding diseases early, planning treatments well, and tracking eye health over time.
Synonyms: Eye Examination Devices, Fundus Scopes
4. Ear Examination Devices:
Description:
Otoscopes are key medical tools that doctors use. They help doctors see the outer and middle part of the ear and the eardrum. These instruments are important for spotting different ear problems. They’re must-have tools for ear doctors and general check-ups.
Key Features of Ear Examination Devices (Otoscopes):
Visualization of the Ear Canal:
An otoscope lets doctors look inside your ear. They check for strange things, blockages, or if you’re sick. It’s super handy for catching ear infections, stuck earwax or foreign stuff inside the ear.
Magnification and Illumination:
An otoscope, armed with a magnifying glass and a light, sheds bright, exaggerated light on ear parts. It helps find even small problems in the ear by closely examining it.
Tympanic Membrane Examination:
An otoscope lets doctors examine your eardrum up close. They can check it’s healthy and see its color and movement. If your eardrum is different, it may have a hole in it. Or there could be fluid behind it. This could point to something wrong in your middle ear.
Detection of Ear Infections:
Devices used to check ears are key in finding everyday ear infections. These include otitis externa (an infection in the outer ear) and otitis media (an infection in the middle ear). You can spot things like swelling, redness, or pus with an otoscopic check.
Evaluation of Hearing Health:
Otoscopes play a key role in checking ear health. They examine the ear’s overall state and spot any problems that might mess with hearing. This is especially important when looking after kids. Ear infections can harm their hearing.
Education and Training:
With otoscopes, both students and medical workers can practice doing ear checks. Such tools give them an actual feel of what normal and not-normal ears look like.
Devices for checking ears are key to good ear health. They’re very important in finding and taking care of issues tied to the ear. With these tools, medical workers can quickly and effectively help those with ear issues.
Synonyms: Otoscopes, Ear Inspection Instruments
5. Heart Activity Monitors:
Description:
Electrocardiographs pick up the heart’s electric signals to check heart rhythm and uncover any heart problems.
These devices, also known as heart activity trackers or ECG machines, are important for doctors. They read and capture the heart’s electrical activity. ECG machines help figure out heart troubles, keep an eye on heart health and check if treatments work.
Key Features of Heart Activity Monitors:
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Recording:
Heart monitors record the electric signals from each heartbeat. This data becomes an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It shows us a picture of the heart’s electric patterns over time.
Heart Rate Measurement:
ECG machines take the heart’s speed through looking at the time gaps between heartbeats. This data is key to study how the heart works. It spots any unusual heart rhythms too.
Rhythm Analysis:
Heart monitors are tools doctors use to study how a heart beats. They’re super important! They can find things like arrhythmias, slow or fast heart beats, and other issues with how a heart rhythm works.
Detection of Abnormalities:
The monitors are critical for spotting unusual heart patterns. They can detect stuff like ischemia and heart attacks, as well as other issues that affect the ECG waveform.
Assessment of Heart Chamber Function:
ECG machines help measure your heart’s size and how it works. Any changes in the ECG graph can tell us about conditions like enlarged or stretched heart chambers.
Monitoring Drug Impact:
Heart monitors measure medication effects on heart rhythm. Useful for heart disease treatment, as ECG changes show drug success or side effects.
Heart monitors are key in heart medicine. They give rich data for diagnoses, management, and prevention of heart disease. These tools give a full review of heart health, serving a crucial part in patient care.
Synonyms: ECG Machines, Cardiac Activity Monitors
6. Temperature Measurement Devices:
Description:
Thermometers are employed across various care levels, from routine physical exams to emergency triage, providing swift and accurate temperature measurements.
Synonyms: Temperature Gauges, Fever Detectors
These commonplace diagnostic medical instruments are integral for healthcare practitioners in diagnosing and monitoring diverse medical conditions.
Sources: We uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
- MedlinePlus. Breath sounds.
- Handler J. The importance of accurate blood pressure measurement. Perm J. 2009;13(3):51-54. doi:10.7812/tpp/09-054
- Shahbabu B, Dasgupta A, Sarkar K, Sahoo SK. Which is more accurate in measuring the blood pressure? A digital or an aneroid sphygmomanometer. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(3):LC11-4. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2016/14351.7458
- Kang HK, Luff AJ. Management of retinal detachment: a guide for non-ophthalmologists. BMJ. 2008;336(7655):1235-1240. doi:10.1136/bmj.39581.525532.47
- MedlinePlus. Otoscope examination.
Dr.Sono. Portable Ultrasound Scanner